how to find wavelength with only frequency
All electromagnetic radiation is calorie-free, and information technology occurs over an extremely wide range of wavelengths, from high-energy gamma waves with shorter wavelengths to low-free energy radio waves with longer wavelengths. But the human centre can detect just a small-scale portion of the radiation, and that portion is referred to as visible calorie-free. In an electromagnetic spectrum, the visible spectrum lies in between the infrared spectrum and the UV spectrum. Visible light ranges betwixt a wavelength of 400 nm and 700 nm. The homo eye cannot find other electromagnetic radiations every bit the radiations has either large or minor wavelengths and is out of biological limitations.
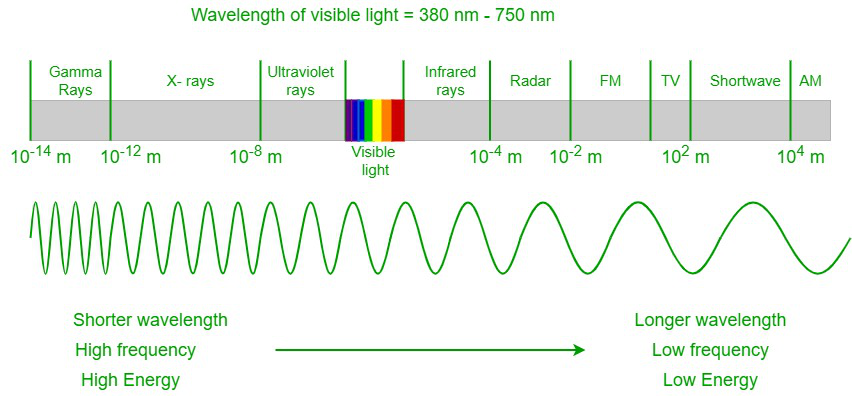
Electromagnetic spectrum
When a visible spectrum travels through a prism, the light gets separated into a spectrum of colors of different wavelengths. The violet color has the shortest wavelength of around 380 nm, and the red color has the longest wavelength of around 700 nm. Our eyes tin can detect the outer-most layer of the sun, the corona, in visible light.
Wavelength
A wavelength is i of the backdrop of a wave and is defined as the distance betwixt the 2 successive crests or troughs of a wave, where a crest is the highest bespeak of the wave, and a trough is the everyman point of the moving ridge. Since wavelength is a altitude or length between 2 points, it is measured in meters, centimeters, millimeters, micrometers, etc. It is denoted by the symbol Lambda 'λ'.

Wave
Frequency
Frequency (f) is divers as the total number of wave cycles or oscillations produced per unit of time. Frequency is measured in terms of Hertz (Hz) or due south-1.
The formula for the frequency:
Frequency (f) = 1/period(T)
f = one/T
- A period is defined equally the time taken to complete an oscillation.
- From the equation of frequency, we can conclude that the frequency of a moving ridge is inversely proportional to its menstruum.
- 1 Hertz = 1 oscillation/second
Wave velocity
The velocity of a wave or moving ridge velocity is divers as the distance traveled by the wave in a unit of time. The S.I. unit of wave velocity is ms-1.
- Lite travels with a speed in the vacuum of 29,97,92,458 m/s, i.east., approximately 3 × tenviii k/s, and it is represented by the symbol c.
Wavelength of the light
We know that light possesses the characteristics of both a moving ridge and a particle. So, the wavelength of a low-cal wave is given as;
λ =
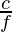
Where λ is the wavelength of light
c is the velocity of light and
f is the frequency of the light
The energy of a photon is given as,
Eastward = h × f =
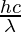
Where E is the free energy of a photon
h is the Planck'due south constant i.east., h = 6.64 × ten-34 joule-second
Wavelength, Frequency, and Energy of the visible light spectrum
| Color | Wavelength | Frequency | The free energy of a photon |
| Violet | 380 – 450 nm | 668-789 THz | 2.75 – 3.26 eV |
| Blue | 450-495 nm | 606-668 THz | 2.fifty – ii.75 eV |
| Green | 495-570 nm | 526-606 THz | ii.17 – 2.50 eV |
| Yellow | 570-590 nm | 508-526 THz | 2.ten – 2.17 eV |
| Orange | 590-620 nm | 484-508 THz | 2.00 – two.10 eV |
| Carmine | 620-750 nm | 400-484 THz | 1.65 – 2.00 eV |
Sample Problems
Problem 1: Summate the wavelength of the visible light with a frequency of 5.36 × 1014 Hz.
Solution:
Given the frequency of light = 5.36 × 1014 Hz
We know, that the velocity of light (c) = 3 × 10eight yard/southward
Now, the wavelength of light (λ) =
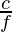
⇒ λ =
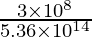
⇒ λ = v.60 × x-7 m
Hence, the wavelength is 5.60 × 10-7 g
Problem ii: If a microwave oven emits microwave free energy of 1.64 × 10-24 J, then calculate the wavelength of the microwave emitted.
Solution:
Given information,
The energy of microwave emitted = 1.64 × x-24 J
Nosotros know, that the energy of a photon =
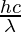
h = 6.64 × 10-34 joule-second
⇒ 1.64 × x-24 =
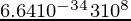
⇒ λ =
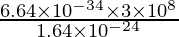
⇒ λ = 12.146 × ten-ii yard = 12.15 cm
Hence, the wavelength of the microwave emitted is 12.xv cm.
Trouble 3: If a radio station broadcasts at a frequency of 555 kHz, then calculate the wavelength of radio waves emitted.
Solution:
Given,
Frequency of radio waves = 555 KHz
Nosotros know, that the velocity of calorie-free (c) = iii × tenviii k/southward
Now, the wavelength of light (λ) =
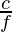
⇒ λ =
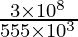
⇒ λ = 540 yard
Hence the wavelength of radio waves emitted is 540 1000.
Problem iv: Calculate the wavelength of yellow calorie-free emitted from a sodium lamp at a frequency of 5.15 × ten14 Hz.
Solution:
Given,
The frequency of xanthous light = 5.15 × 10fourteen Hz
Nosotros know, that the velocity of light (c) = iii × 108 m/due south
Now, the wavelength of light (λ) =
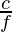
⇒ λ =
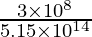
⇒ λ = 582.v × ten-9 m = 582.5 nm
Hence, the wavelength of the yellow lite is 582.5 nm.
Problem 5: Calculate the wavelength of a photon with an free energy of 3.35 × 10-19 Joules.
Solution:
Given,
The free energy of a photon = 3.35 × 10-19 Joules.
We know, that the free energy of a photon =
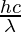
h = half dozen.64 × x-34 joule-2d
⇒ iii.35 × 10-19 =
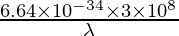
⇒ λ =
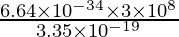
⇒ λ= 5.94 × 10-7 m = 594 nm
Hence, the wavelength of the photon is 594 nm.
Trouble 6: The broadcasting frequency of a radio station is 101 MHz. What volition exist the wavelength of the wave if the broadcast wave is an electromagnetic wave?
Solution:
Given data, Frequency of the wave = 101 MHz = 101 × 10half dozen Hz
Speed of low-cal = 3 × 108 m/s
Now, the wavelength of calorie-free (λ) = c/f
⇒ λ = (3 × ten8)/(101 × x6)
⇒ λ = 2.97 one thousand
Hence, the wavelength of the broadcast wave is 2.97m
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/how-to-calculate-the-wavelength-of-the-light/
Posted by: sheppardforgiagether.blogspot.com

0 Response to "how to find wavelength with only frequency"
Post a Comment